An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a software or hardware tool that monitors network or system activities for malicious or unauthorized behavior. IDS plays a vital role in cybersecurity, as it can detect and alert security administrators of potential attacks, breaches, or vulnerabilities. IDS technology has advanced significantly, with the use of large data analytics, machine learning, and AI to improve the accuracy, efficiency, and scalability of intrusion detection.
This article will explicate, how does intrusion detection systems work in 2023 and the types of intrusion detection systems. Why are intrusion detection systems important?
What is an intrusion detection system?
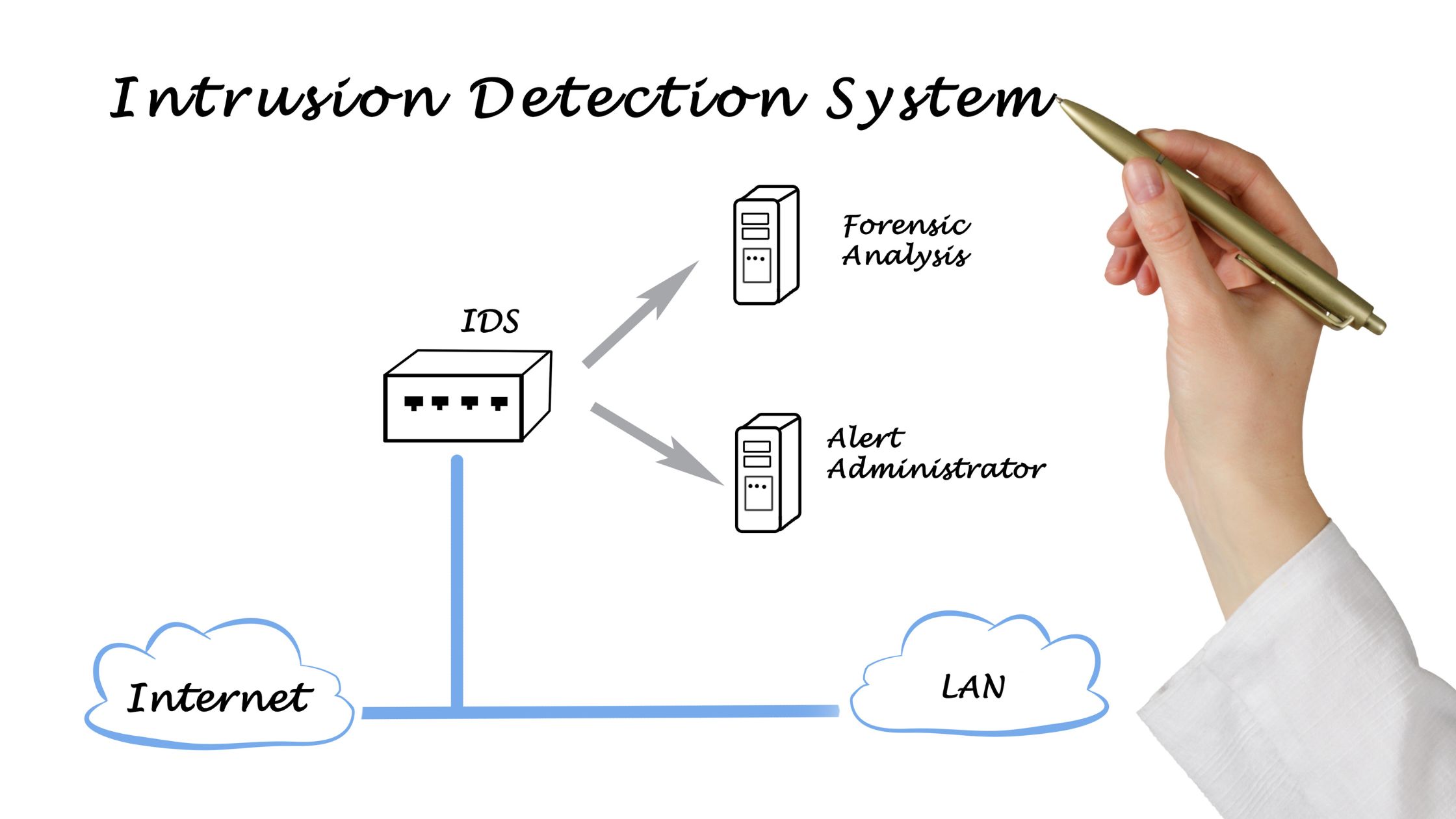
IDS or Intrusion Detection System is a technology that takes care of traffic for unusual activities and issues notifications when found. IDSs are passive monitoring tools that can identify possible threats. This smart intrusion detection system can also send out notifications to incident personnel in Security Operations Centers (SOCs). SOCs will then look into and address the potential event. The IDS system does not offer any real endpoint or network protection.
An IDS’s major duties are anomaly detection and reporting. However, certain IDSs are equipped to respond to suspicious or abnormal traffic by blocking traffic coming from suspect internet protocol addresses. IDS is specially designed to monitor network traffic and spot anomalies. Unexpected and inexplicable network changes could be signs of malicious activity at any level, from the start of an assault to a full-blown breach.
IDSs can assist with compliance initiatives as well. Organizations must deploy intrusion detection measures in accordance with some rules. Such as, PCI-DSS also known as, Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard.
Why are intrusion detection systems important?
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) are essential tools for defending pc networks from unauthorized access and malicious attacks. IDS can reveal network traffic and become aware of suspicious activities, such as port scanning, denial-of-service attacks, or malware infections. For example, if an IDS detects that a host is sending a massive variety of packets to unique ports on some other host, it may also indicate that the first host is trying to discover an open port to exploit a vulnerability. IDS can additionally alert community directors or take preventive actions, such as blocking off the supply of the attack or keeping apart the compromised host. By using IDS, network safety can be stronger and conceivable damage can be minimized.
Network Intrusion Detection System has the ability to recognize security issues. Organizations get a number of advantages from the IDS system. IDS can analyze varieties of attacks regardless of the quantity. By using this knowledge, organizations can modify their security protocols or set better security measures. Companies can find defects or issues with the configurations of their network devices with the use of an intrusion detection system. Then, upcoming risks can be evaluated through these metrics.
Organizations can also use Intrusion Detections System to achieve regulatory compliance. With an IDS, businesses have better network visibility, which makes it simpler to adhere to security standards. Businesses can also utilize their IDS logs only as a part of the documentation to demonstrate that they are complying with legal standards.
Intrusion detection systems can enhance security responses. IDS sensors can identify network devices and hosts. Therefore, it can also analyze data within network packets and detect operating systems. It can be considerably more effective to utilize an IDS to gather this data than to manually count all linked systems.
How does intrusion detection system work?
We have yet to understand a lot regarding IDS, now the question is how does Intrusion Detection System work. The IDS system can be specialized into anything. Such as a hardware item that is connected to the network or software programs deployed on endpoints. There are some IDS options that are offered as cloud services. Such as,
Signature-based Detection
Signature-based detection is a cybersecurity technique that uses footprints or unique identifiers to detect malware. It compares network traffic statistics to a database of known malicious signatures and generates an alert when a fit is made. However, it faces challenges such as not detecting new or unknown threats that are no longer part of current databases. Cybercriminals continuously evolve their malware to avoid signature detection, using techniques like encryption, obfuscation, polymorphism, or metamorphism. Additionally, signature-based detection can generate false positives or false negatives, which can waste resources and cause alert fatigue.
To overcome these limitations, signature-based detection systems can be integrated with threat intelligence feeds, which provide up-to-date records on current and emerging threats. These feeds help signature-based detection systems update their databases more accurately, identify new or unknown threats based on behavior or context, and reduce false positives or false negatives by providing more granular and precise signatures that match the malware’s characteristics. By integrating threat brain feeds, signature-based detection systems can enhance their capabilities and effectiveness.
Anomaly-based Detection
Anomaly-based detection is a method of identifying malicious activities on a network by comparing them with a baseline of normal behavior. Anomaly-based detection uses machine learning and behavioral analysis techniques to learn the patterns of normal network traffic and flag any deviations from them. Anomaly-based detection faces the challenge of reducing false positives and false negatives, which are alerts that either wrongly identify benign activities as malicious or fail to detect actual attacks.
Heuristic-based detection
Heuristic-based detection is a method of identifying malicious software by analyzing its code for suspicious features. Unlike signature-based detection, which relies on comparing code to a database of known malware samples, heuristic-based detection can detect new and unknown threats that have not been recorded before. Heuristic-based detection uses rule-based and pattern-matching algorithms to examine the code and look for anomalies that indicate malicious behavior.
For example, heuristic-based detection can flag code that tries to overwrite files, replicate itself, or hide from antivirus programs. Heuristic-based detection can also adapt to evolving attack techniques by learning from previous encounters and updating its rules and patterns accordingly.
Types of intrusion detection systems
There are 5 types of intrusion detection systems available till now. They are,
NIDS (network intrusion detection system)
The first kind of IDS is NIDS which is also known as Network Intrusion Detection System. NIDS is installed at a predetermined location within the network. It then monitors all network traffic coming from all connected devices. NIDS carries out an observation of all subnet traffic and contrasts it with a database of known attacks.
HIDS (host-based intrusion detection system)
Another kind of IDS is HIDS. It is also known as Host Intrusion Detection System. These are network applications that run on separate hosts or gadgets. HIDS can only monitor the outgoing and incoming packets from the device. This notifies the administrator of any unusual or malicious behavior. It compares the current snapshot of the system files with the prior snapshot. An example of a HIDS is Tripwire, which can detect changes in files and directories.
IDS (protocol-based intrusion detection system)
Next comes the PIDS. It is also known as a Protocol-based intrusion detection system. This network consists of a system that is permanently installed at the server’s front end. This front controls and interprets the protocol used by users and devices to communicate with the server. PIDS continuously monitors the HTTPS protocol stream and receives the associated HTTP protocol in an effort to secure the web server.
APIDS (application protocol-based intrusion detection system)
Then comes APIDS. APIDS is also known as an Application Protocol based Intrusion Detection System. This is generally set within a server cluster. It detects intrusion by analyzing and observing communication on application-specific protocols. For example, an APIDS can detect attacks on a web server by analyzing the HTTP requests and responses. APIDS is usually deployed in a server cluster environment.
Hybrid IDS (hybrid intrusion detection system)
Hybrid IDS is also known as Hybrid Intrusion Detection System. It is built by combining two or more intrusion detection system methodologies. The host agent in the hybrid intrusion detection system is merged with network data, to create a comprehensive picture of the network system.
Among these 5 IDSs, the most effective one is the Hybrid IDS. An example of a hybrid IDS is demonstrated by the prelude, which integrates various IDS technologies into a single framework.
Intrusion Detection System Challenges and Future Trends
The field of cybersecurity faces many challenges and opportunities in the coming years. Some of the prime factors that will shape the future of cybersecurity are:
Evolving threat landscape and sophisticated attacks
Cybercriminals are constantly developing new techniques and tools to exploit vulnerabilities and compromise systems. They use advanced methods such as ransomware, zero-day attacks, and supply chain attacks to target organizations and individuals.
For example, in 2021, the Colonial Pipeline was hit by a ransomware attack that disarranged the supply of fuel in the US. In 2020, the SolarWinds hack compromised the networks of several government agencies and private companies.
Privacy concerns and compliance issues
As more data is collected and stored online, the risk of data breaches and identity theft increases. Organizations need to comply with various regulations and standards to safeguard the privacy and security of their customers and employees. They also need to balance the trade-off between security and usability.
For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union imposes strict rules on how private data can be processed and transferred. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) allows consumers more control over their data.
Integration with cloud environments and IoT devices
The adoption of cloud computing and IoT devices has increased the complexity and diversity of the cyberattack surface. Organizations need to secure their cloud infrastructure and applications, as well as their IoT devices and networks. They also need to manage the risks associated with third-party vendors and service providers.
For example, in 2019, a hacker gained access to a database hosted on Amazon Web Services (AWS) that contained the personal information of millions of Capital One customers. In 2018, a botnet called Mirai infected millions of IoT devices and launched distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
Advancements in machine learning and AI for enhanced detection
Machine learning and AI can help improve the detection and response capabilities of cybersecurity systems. They can analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns and anomalies, and automate tasks. However, they also pose new challenges such as adversarial attacks, bias, and explainability.
For example, adversarial attacks are designed to fool machine learning models by introducing subtle changes in the input data. Bias can result from flawed data or algorithms that discriminate against certain groups or individuals. Explainability refers to the ability to understand how machine learning models make decisions.
Importance of collaboration and information sharing
Cybersecurity is a collective effort that requires collaboration and information sharing among various stakeholders. Organizations need to share threat intelligence altogether, as well as with government agencies and industry associations. They also need to nurture a culture of trust and cooperation within their own teams.
For instance, the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA) in the US encourages the voluntary sharing of cyber threat indicators between the public and private sectors. The Cyber Threat Alliance (CTA) is a global network of cybersecurity organizations that share threat intelligence and best practices.
Difference between firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Firewalls and IDS are two cybersecurity tools that can be used to safeguard a network or endpoint. However, their objectives are very different from one another.
IDSs are passive monitoring tools that identify possible threats and send out notifications to incident responders or analysts in SOCs. SOCs may look into and address the potential event. An IDS offers no real endpoint or network protection.
On the other hand, a firewall is intended to serve as a defense mechanism. It analyzes the metadata contained in network packets and decides whether to let or prohibit traffic based on pre-established rules. This established a barrier that prevented some traffic or protocol types from crossing.
Since a firewall is an active security measure, it is more comparable to an IPS than an IDS. Similar to an IDS an IPS actively stops threats rather than only issuing alarms. This act enhances a firewall’s functionality, and various next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) include integrated IDS/IPS. This allows them to implement the predetermined, filtering rules (firewall) as well as to identify and react to more advanced cyber threats (IDS).
Conclusion
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) are essential equipment for protecting networks and structures from cyberattacks. They can monitor, analyze, and alert on malicious things to do and anomalies in real-time. Some of the key factors discussed in this document are:
- The sorts and functions of IDS, such as network-based, host-based, and hybrid IDS.
- The benefits and challenges of IDS, such as improving the protection posture, reducing false positives, and coping with advanced threats.
- The high-quality practices and recommendations for deploying and maintaining IDS, such as deciding on the right IDS for the environment, tuning the IDS regulations and signatures, and updating the IDS regularly.
IDS are not a silver bullet for cybersecurity, however, they are an integral aspect of a defense-in-depth strategy. As cyberattacks emerge as extra sophisticated and frequent, IDS will proceed to play an important position in detecting and responding to them.



