A DNS server helps to access the internet. It means a user accesses the website and online services without facing the complex strings of numbers. It is a hierarchical structure of name resolution. The DNS server is the address book of the World Wide Web. It incorporates the IP tackle for each website on the internet.
In this article, we’ll explore what DNS is and what DNS servers are. How Does It Work?
What is a DNS, and How Does It Work?
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It is the phonebook of the internet. A person accesses a website by domain names, like ESPN.com. A web browser interacts through IP addresses. A DNS system converts domain names into IP addresses, allowing a browser to load internet resources. Most of the devices are connected to the internet with unique IP addresses. DNS servers reduce the problem for humans to memorize IP addresses.
DNS works via querying a community of servers that store the mappings between domain names and IP addresses. DNS can be seen as the phonebook of the internet, as it lets customers access websites barring memorizing numerical addresses.

What is a DNS Server?
A server is a program or a device dedicatedly to working with services. It refers to “clients”. In this modern world, DNS clients are built into the PC and Smartphone operating systems. It helps to enable web browsers to interact with the DNS servers.
Once the DNS server connects the IP tackle, then browsers take the addresses and send the facts to CDN ( Content Delivery Network) beginning servers. After completing this process, the information on the website can be accessed by the user. The DNS server starts the manner by discovering the IP tackle for the website URL (Uniform Resource Locator).
How Does a DNS Server Work?
The Domain Name System works by saving a database of domain names and their IP addresses. This database distributes across many different servers.
The top server is the root server. There are 13 root servers in total. They are responsible for saving the names of all the top-level domains (TLD), like .com, .net, and .org.
When you make a DNS request, it will first contact a root server. It sends your request to the TLD server. The TLD server will direct your request to the trustworthy DNS server for the domain name.
That trustworthy DNS server is the final destination for your DNS request. It will return the IP address for the domain name you are trying to reach.
Types of DNS Servers
If your computer can no longer discover a matching IP address in your host file, then it will publish your DNS query to a community f four DNS servers.
- DNS Resolver: It plays the primary role of an intermediary between a computer and other DNS servers. It helps to pass a request to another domain name system server and send it back once fulfilled.
- Root Nameserver: It is also known as the root DNS server. It provides directions on how to locate it. When the root nameserver receives a request from the DNS resolver, it will identify the top-level domain of the domain name. Then it tells the resolver to go in the right direction of the TLD nameserver.
- TLD Nameserver: It is a server function that is responsible for managing information about domain names that use a specific top-level domain. A TLD, such as .com, .org, .online, and .net, is the final part of a domain name.
- Authoritative Nameserver: It is the final process of the DNS resolution process. It saves all information that is related to your visited domain name, including IP addresses. The resolver will secure the IP address and send it back to your PC to direct you to the site.
How to Choose the DNS Server?
There are many different DNS servers available. In that case, it is difficult to choose the right one. There are a few things to consider before choosing the DNS server:
- Reliability: Make sure the DNS server is reliable and good uptime record.
- Performance: Make sure the DNS server is fast and can handle a high volume of requests.
- Security: Make sure the DNS server is secure and protects your privacy.
Popular DNS Servers
A DNS allows you to communicate with a computer so that you can visit multiple places on the web. In that case, DNS servers play an important role in this.
- Google Public DNS: This is the free and public DNS server. It is also known for reliability and performance.
- Cloudflare DNS: This is another DNS server that is free and public. It offers a number of features, including security and performance.
- Open DNS: It is the most unique and paid DNS. it offers a variety of features, including parental controls and content filtering.
What are the Types of DNS Queries?
DNS has three types of queries that occur. A DNS resolution process that is optimized can reduce the distance traveled by using a combination of these queries. In the best world, a DNS title server would be in a position to respond to a non-recursive question thanks to cached record data.
3 types of DNS queries:
- Recursive query: DNS client requires a DNS server. When the resolver can not find the record, the resolver will respond to the client with the requested resource record.
- Iterative query: The DNS customer lets the DNS server return the nicest reply it can. A referral to a DNS server is reliable for a lower level of the domain name space, returned if the DNS server does not have a match for the query name. The referral address will then be contacted by the DNS client. The procedure is repeated with additional DNS servers until an error or timeout occurs.
- Non-recursive query: This usually happens when a DNS resolver client asks a DNS server for a record that the server already has access to, either due to the fact that the server is authoritative for the file or due to the fact that the report is already in the server’s cache. Typically, a DNS server will cache DNS documents to decrease upstream servers and extra bandwidth usage.
What causes DNS Server Not Responding?
DNS server not responding is a common error that occurs when your computer cannot connect to the internet. There are several feasible motives for this problem, such as:
- Your DNS settings are incorrect or outdated.
- Your router or modem is malfunctioning or needs to be restarted.
- Your firewall or antivirus software is blocking the DNS requests.
- Your ISP or network provider is experiencing issues or performing maintenance.
How to Fix DNS Server Not Responding?
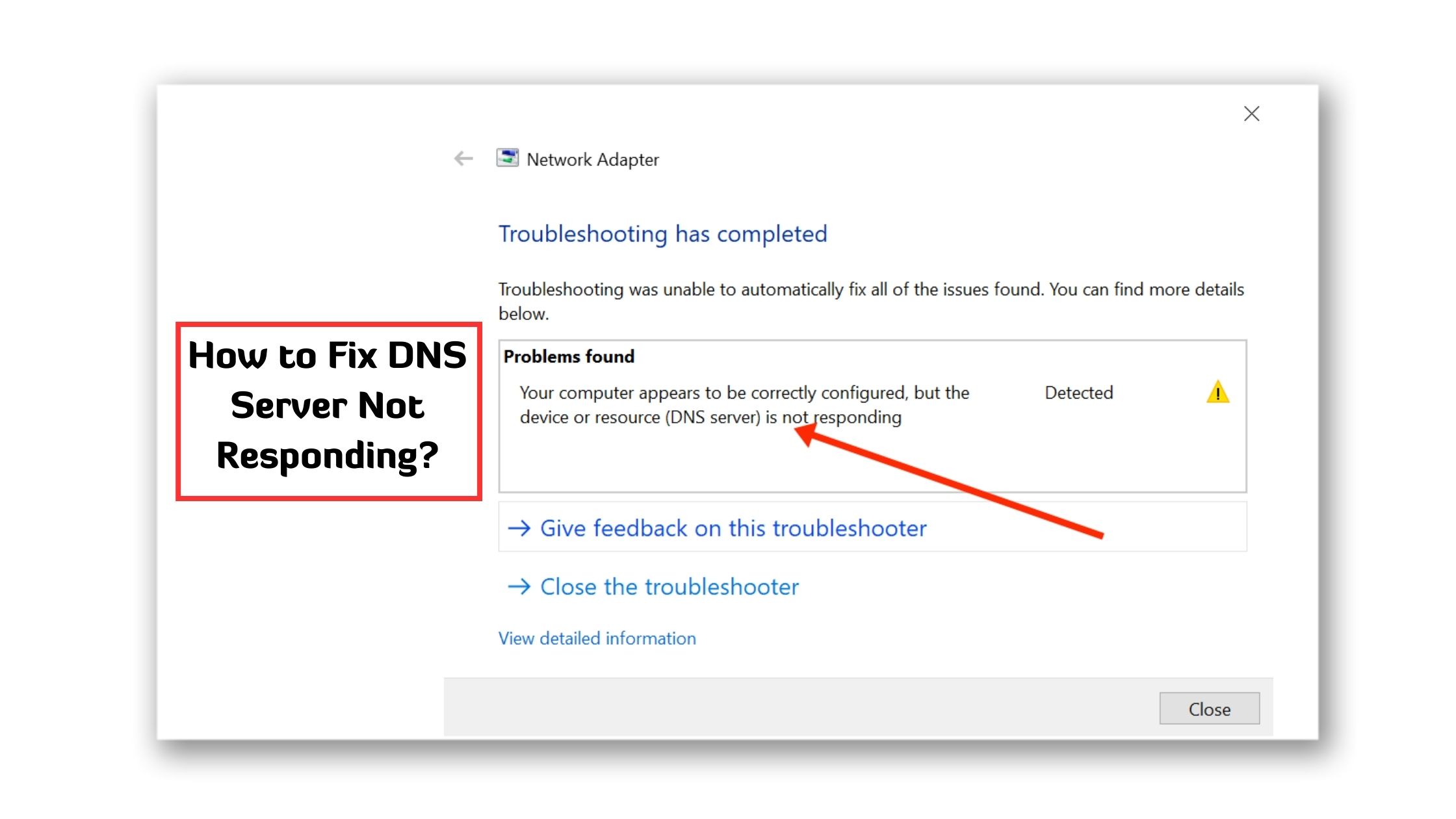
There are some steps to fix the “DNS Server Not Responding” error:
- Use multiple web browsers
- Accessing a website with a different device.
- Look into possible network issues
- Clear the DNS cache
- Disable IPBV6
- Deactivate your firewall and antivirus temporarily.
- Reset DNS settings
- Update the network adapter driver
- Disable all network connections except the internet connection.
- Restart the computer in safe mode.
What is DNS caching?
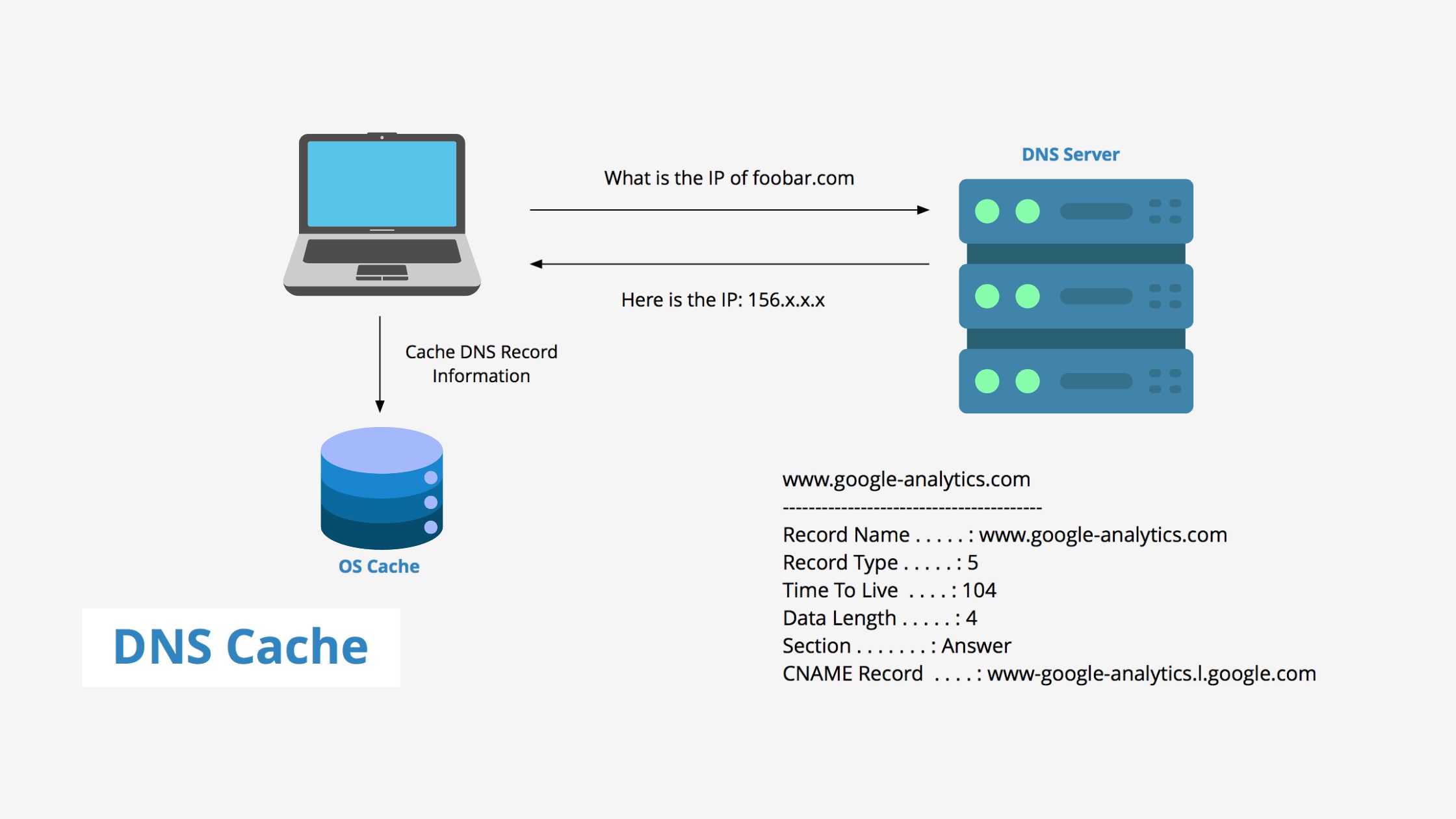
So that you can speed upwards load instances and utilize less bandwidth and also CPU, DNS caching requires storing data near the client, which makes the particular request so your DNS query may be resolved sooner, and further DNS lookups may be avoided. There are numerous places in which DNS data may be cached, and every one of those places helps keep DNS records to get a specific time frame determined by way of a time-to-live (TTL).
Conclusion
The particular DNS system can be an important area of the Internet. It lets you type simple websites into Internet Explorer. If you’re not happy with your DNS server along with your ISP, you can replace them with a new set of DNS servers. There are usually many community DNS computers available, and so they offer several benefits, just as faster DNS queries, a higher level of privacy, and far better security.
FAQ
-
What is DNS over HTTPS (DoH)?
DNS resolution over an HTTPS connection that is secure. Between a stub resolver and a recursive resolver, DNS over HTTPS significantly improves privacy and security. It also works in conjunction with DNSSEC to offer end-to-end authenticated DNS lookups.
-
What is TTL?
Your DNS record’s time to live (TTL), which is measured in seconds, is how long it will remain cached when nameservers are resolved online. It is advised to set your TTL to a lower value in order to reduce this cache time if your IP is dynamic (changes frequently) or if you intend to move your computer to another IP. It is advised to change your TTL to a higher value once your IP is on a static IP or after you have moved your system to the new IP.
-
What is Dynamic DNS?
Applications that typically require a static IP address can be accessed by a client connecting to the internet with a dynamic lP address thanks to a dynamic DNS service. Users can host web servers, email servers, or FTP servers with the help of this feature.
-
Can DNS Stop Internet Connection?
DNS can stop an internet connection if there is a problem with the DNS server, such as being down, overloaded, or misconfigured. If the DNS server cannot resolve the domain name to an IP address, the browser will not be able to connect to the website. To fix this issue, one can try using a different DNS server, clearing the DNS cache, or restarting the router.
-
What is a DNS server in WIFI?
A DNS server is a device that translates domain names into IP addresses. When you connect to a WIFI network, your device usually obtains the DNS server settings from the router or the access point. This allows you to access websites and other online services by their names instead of their numerical addresses.