A firewall can function in hardware, software, SaaS, and public or private cloud. It is a computer network security device that can restrict internet entering, leaving, or moving within a private network. By manually blocking or allowing data packets, this device executes its purpose. Its primary goal is to deter harmful acts and stop anyone, outside or inside of a private network from performing unlawful web activities. Firewall has its own distinctive way to direct. Let’s dive into the following article and find out more about Firewalls and types of firewalls!
What Is a Firewall?
A firewall is also known as a network firewall. It is a kind of cybersecurity tool to filter inbound and outbound traffic. Its main purpose is to prevent unwanted access to servers, applications, and networks. Even Though a firewall can simply restrict attempted connections, every application should have its own authentication system.
Firewalls are security tools that keep unauthorized users out, enhancing network security and resource availability. Firewalls however do not guarantee complete protection. It is only one aspect of a larger information security infrastructure.
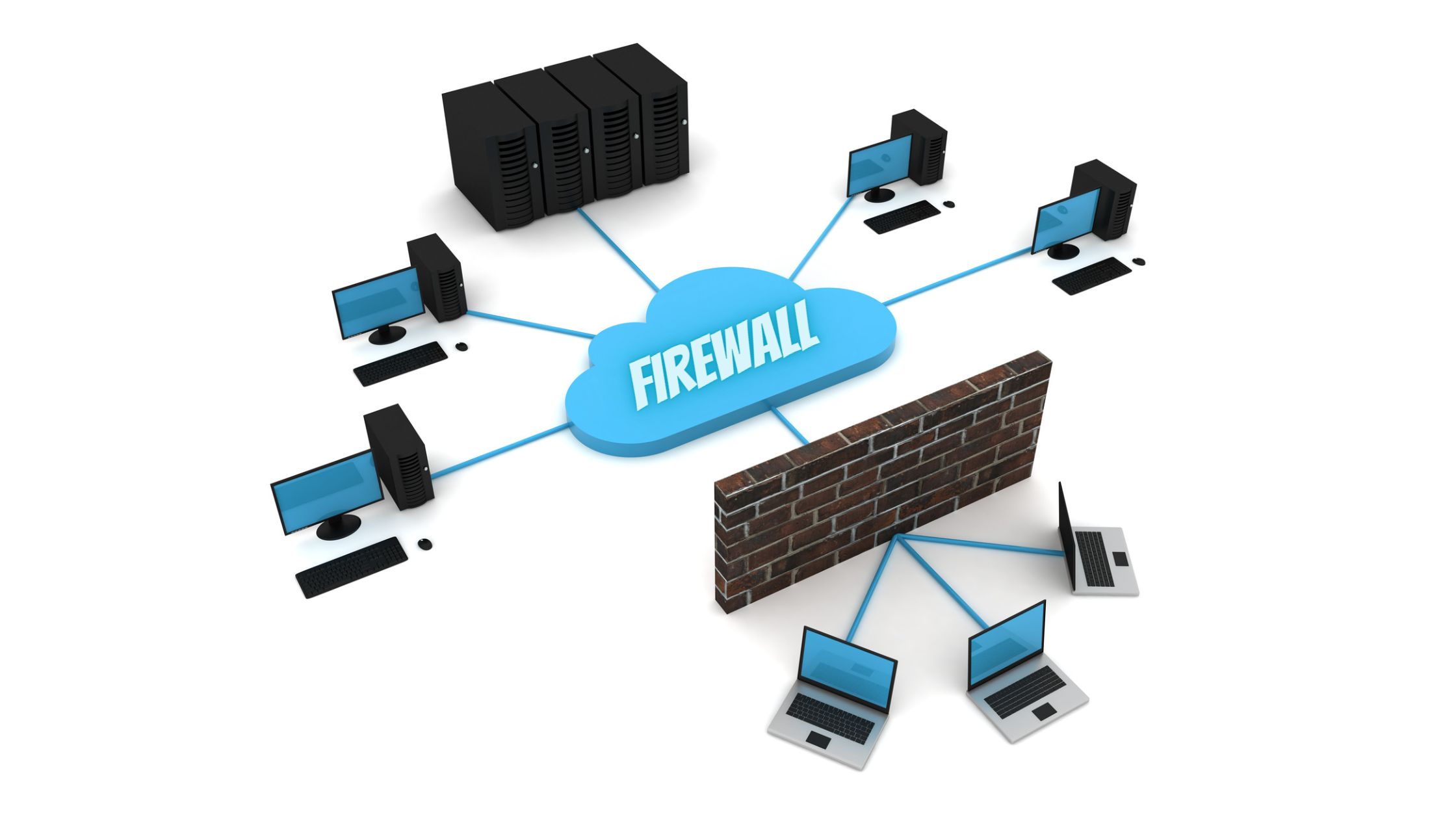
How Does a Firewall Function?
Firewall filters traffic, ensuring trusted and dangerous connections in web-based networks. Firewalls protect private networks and network hosts. Networks access the internet through subnetworks for security and privacy. The followings are the fundamental subnet segments:
- The public or global internet or numerous extranets are often referred to as external public networks.
- Home networks, company intranets, and other “close” networks are all considered internal private networks.
- Broader networks with computer or bastion hosts with enhanced security that are prepared to withstand an external attack, are described by perimeter networks.
A network can be divided using specialized gateway computers called screening routers. On the network level, they are referred to as home firewalls. Two most common section models are screened host and screened subnet firewall:
- A single screening router connects the internal and external networks in screened host firewalls. The two subnetworks of this architecture are these networks.
- Two screening routers are used by screened subnet firewalls. One serves as an access router between the perimeter and external network and the other as a blockage router between the perimeter and internal network.
A firewall can be installed on the host machines as well as the network perimeter. It is positioned between a single computer and its link to a private network in order to do this.
- Network firewalls regulate traffic between external and internal networks using hardware, software, or virtual appliances.
- Host firewalls protect individual devices and private network endpoints by regulating traffic to and from specific applications, allowing content management.
Network firewalls require broad configuration, host firewalls tailored for specific needs, ideal for multi-layer security systems.
The firewall filters traffic using pre-set rules for private network and device control. All firewalls, regardless of kind, may filter using a mix of the following:
- Source
- Destination
- Contents
- Pocket protocols
- Application Protocols
IP addresses and ports communicate devices, ensuring secure communication and avoiding issues.
A firewall can decide whether to forward or quietly discard a data packet that attempts to establish a connection by using these identifiers.
Why is a Firewall Necessary?
Computers are protected by Firewalls against malicious software. Such as Viruses, spyware, and malware. Firewall also has many other necessities besides this. A brief explanation has been given below!
The Macro Virus:
A macrovirus is an assault program that is concealed in commonplace programs such as Microsoft Word, zoom, or even sticky notes. When a victim launches and uses the application, the malicious code gets activated.
Lost or Tampered with Data:
Devoted hackers can easily break through common passwords and acquire their targets’ login information in a matter of seconds.
Accessing Backdoor:
Attackers can access computer systems through backdoor access. It is an unreported method. High-security dangers result from this since attackers can use it to download files as well as carry out actions from a distance.
Attacks on access:
Hackers attempt to get access to another user’s network or account during an access attack using a variety of techniques. Such as guessing passwords.
Attempts to Deny Service:
DoS attacks aim to bring a network to a halt by saturating it with unsolicited traffic. A social network company’s servers. For instance, could be pounded by attackers, preventing them from handling consumers’ proper connections or requests.
Types Of Firewall

Firewalls come in a wide variety of designs to encounter threats. They are,
VPN Firewalls
A proxy or VPN firewall is a primitive form of firewall device. It acts as the gateway between one network to another for a particular application. BThrough blocking direct connections from outside the network, proxy servers can add security and other features like content caching. However, this might also have an effect on the applications that can be supported throughput capacities. For example, a proxy firewall may block some streaming services or online games that require high bandwidth or low latency.
Firewall with Stateful Inspection
Stateful inspection firewalls are referred to as “traditional” firewalls. It allows or denies traffic based on protocol, port, and state. It keeps track of all activities starting with a connection’s opening as well as ending with it. Administrator-defined rules and context, which refer to utilizing data from prior connections and packets that belong to the same connection, are both taken into consideration while making filtering judgments.
UTM (Unified Threat Management) firewall
A UTM device is a combination of a stateful inspection firewall, intrusion prevention, and antivirus features. Additional services and frequent cloud management could also be a part of it. UTMs emphasize use and simplicity.
NGFW (Next-Generation Firewall)
Firewalls now go beyond simple stateful inspection and packet filtering. To stop contemporary dangers like advanced malware and application-layer attacks, the majority of businesses are implementing next-generation firewalls.
The following features must be present for an NSFW according to Gartner, Inc.
- Stateful inspection combined with intelligence-based access control.
- System for integrated intrusion prevention (IPS)
- Application control and awareness to identify and prevent dangerous applications.
- Upgraded routes to incorporate upcoming information feeds.
Methods for dealing with challenging security risks geolocation and reputation-based URL screening NGFWs can do more, even if these features are fast becoming the norm for most businesses.
Threats-specific NSFW
These firewalls offer enhanced threat detection and remediation in addition to having all the features of a regular NGFW. A threat-specific NGFW allows you to:
- With the knowledge of full context, you will be able to identify which assets are most vulnerable.
- Intelligent security automation sets policies and dynamically hardens your defenses, allowing you to respond to attacks quickly.
- With network and endpoint events correlation, evasive or suspicious behavior can be more accurately detected.
- Retrospective security that continuously checks for questionable activity and behavior even after initial inspection can greatly reduce the time from detection to clean up.
- Unified rules that provide protection along the full attack continuum simplify administration and cut down on complexity.
Virtual fence
To monitor and secure traffic across physical and virtual networks, a virtual firewall is typically deployed as a virtual appliance in a private cloud (VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, KVM) or public cloud (Amazon Web Services or AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform or GCP, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure or OCI). In software-defined networks (SDN), a virtual firewall is frequently a crucial element.
A Cloud-based firewall
 Modernizing application and workload infrastructure security at scale is what cloud-native firewalls are doing. Cloud-native firewalls give networking operations and security operations teams the ability to operate at rapid rates thanks to automatic scaling features.
Modernizing application and workload infrastructure security at scale is what cloud-native firewalls are doing. Cloud-native firewalls give networking operations and security operations teams the ability to operate at rapid rates thanks to automatic scaling features.
Cloud Native Firewalls’ benefits
- an elastic and adaptable security
- capacity for several tenants
- judicious load balancing
Firewalls flaws
As firewalls do not use DPI to thoroughly analyze packets, less advanced firewalls, including packet-filtering firewalls are susceptible to higher-level attacks. In order to solve the risks, NGFWs were developed. However, NGFWs still have problems and are exposed to new attacks. Due to this, businesses should combine them with other security measures like IDPS. Here are some examples of contemporary risks that can expose firewalls:
Internal Strikes
To divide the network and offer internal security, organizations can layer an internal firewall on top of a perimeter firewall. Organizations can audit sensitive data using NGFW features if an attack is suspected. All audits should be evaluated against the organization’s baseline documentation outlining best practices for utilizing the network. The following are some examples of actions that might point to an insider threat:
- sending private information in plain text.
- access to resources after business hours.
- failure by the user to access sensitive resources.
- users from outside parties using network resources.
DDoS (Distributed DoS) attacks
A DDoS attack is a malicious attempt to obstruct a network’s regular traffic by saturating the target or the area around it with a flood of traffic. It uses numerous infected computers as attack traffic sources. Computers and other networked resources, such as Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets, can be exploited by machinery. A DDoS assault is comparable to a backup in ordinary traffic that keeps it from reaching its target. Differentiating between a DDoS attack and regular traffic is the main issue when trying to mitigate one. This attack type frequently involves communication that appears to originate from reliable sources, necessitating cross-checking, and auditing from several security components.
Malware

Malware threats are diverse, intricate, and continually changing, just like the networks that security technology is meant to safeguard. With the growth of IoT, networks are becoming more dynamic and sophisticated, making it more challenging for firewalls to protect them.
Patching and Setting Up
Network security can be harmed by a firewall that is improperly set or by a vendor update that was overlooked. IT administrators need to take the initiative to maintain their security components.
Conclusion
Organizations must be provocative in adopting cutting-edge services for mitigating threats and guaranteeing network security as the cybersecurity landscape continues to change. It can be difficult to distinguish between firewalls given the large range that is offered at the market. However, it is suggested to do your own research to examine the differences and resemblances among the five fundamental types of firewalls.







